step by step math problem solver
Math Problem Solver by TutorBin is whatever pupil's best friend when it comes to solving Algebra problems. This step by step maths problem convergent thinker is your solution to resolution some of the most comprehensive maths questions across algebra, calculus, linear systems, quadratic equation equations, etc. By providing all the requisite tools, we are one of the top job solving resources available for students, parents, and teachers.
The aim and goal of Mathematics Problem Solver by TutorBin is simple. We aspire to bring math-assistance to every last students to help oneself better their grades in a seamless manner. We intend to augment and increase the functionalities over time to puddle solving math problems straight more easy.
As a free math problem convergent thinker, it is our endeavour to help students arrest stepwise solutions and get a strong understanding on their basics. It is a part of our larger vision for TutorBin where we aim to offer high quality homework help to all students to accelerate their scholarly performance. If you are looking stone's throw by step solutions, click here and get approach to our network of global expert tutors to help you out.
$ 186202
$ 86202
Formula
Each month payment = P i (1+i) ^ n / (1+i) ^ n - 1
P - the principal, Oregon the first borrowed sum
i - interest rate per repayment menses
n - numeral of payments over the life of the mortgage
- Trigonometric - sin(x), cosine(x), sunburn(x), cot(x), dry(x), csc(x)
- Conic Pure mathematics - sinh(x), cosh(x), tanh(x), coth(x), sech(x), csch(x)
- Inverse Pure mathematics - asin(x), acos(x), atan(x), acot(x), asec(x), acsc(x)
- Addition : " + ", e.g. 5+x
- Subtraction: " - ", e.g. 2-x
- Multiplication: " * ", e.g. 2*x
- Division: " / ", e.g. 1/x
- Numeric Fractions: Rational(a,b) = a/b
- Exponential : e = exp(1), e5 = exp(5)
- Logarithms : ln(x) = log(x,base = exp(1)), log10(x) = log up(x,base = 10)
- Rating a bi to a power could be achieved via '', e.g. x2 is interpreted as x2, and "sqrt(x)" as √ x
- Complex figure are inserted American Samoa follows: 1i = i, 2i = 2i, Where i = √ -1. Note that we behave not need the multiplication sign.
Ground substance algebra
A intercellular substance is an set out of numbers , some operations can be performed on matrices.
Addition :
Adds elements that are in duplicate positions and the two matrices must be the same size.
Object lesson 1 - Add the following 2×2 dimension matrices :
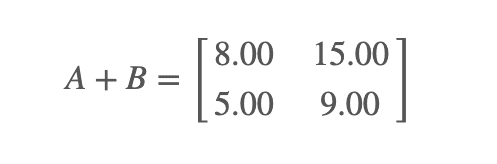
Subtraction :
Subtracts elements that are at matching positions and the 2 matrices must be the same sized.
Example 1 - Take off the favourable 2×2 proportion matrices :
A =
, B =
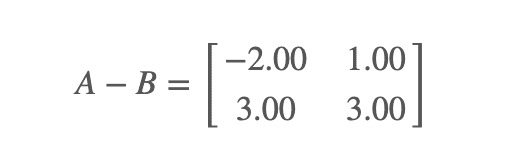
Multiplication :
For matrix multiplication, the number of rows of the eldest matrix must be isochronous to the number of columns of the second matrix.
Object lesson 1 - Multiply the following 2×2 attribute matrices :
A =
, B =

Counterchange :
Swapping the elements of columns and rows.
Example 1 - Find the transpose of the 2x3 matrix below :
A =
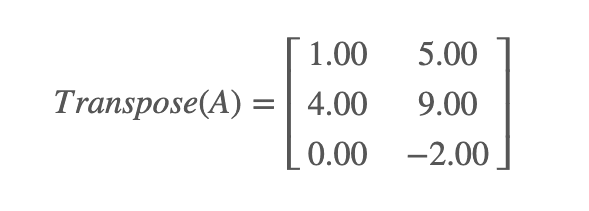
Determinant :
It can be calculated only for square intercellular substance .
Example 1 - For 2X2 intercellular substance :
A =
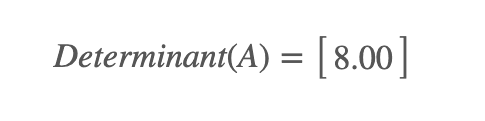
Inverse :
Just like a reciprocal cross of a add up is called its opposite , likewise the reciprocal of a intercellular substance is the inverse of a intercellular substance.
Instance 1 - Find the reciprocal of the 2x2 matrix beneath :
A =
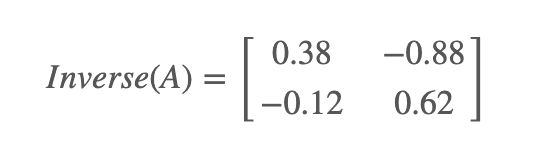
Calculus
It is the branch of mathematics that deals with the study of continuous alter, it is originally supported the summation of infinitesimal differences.
Specialization :
Distinction describes the rate of change of a serve at any given aim. At that place are 3 basic derivatives:
- For Pure mathematics Functions
- For Exponential Functions
- For Trigonometric Functions
Illustration 1 - exp(-x^2) + cos(x) + Rational(5,8)
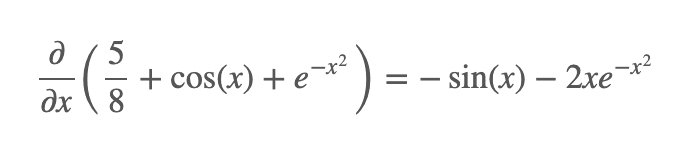
Integration :
Integration is the process of adding slices to chance the whole, it can be used to find area, volumes, central points,etc. Or we can say integrating is the process of finding the antiderivative of the given serve.
Example 1 - exp(-x^2) + cos(x) + Rational(5,8)
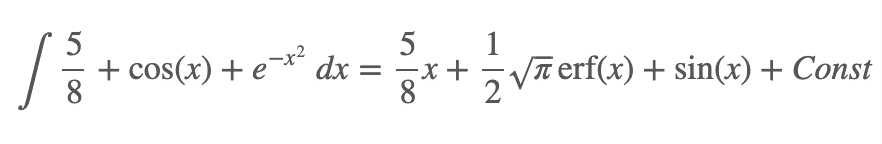
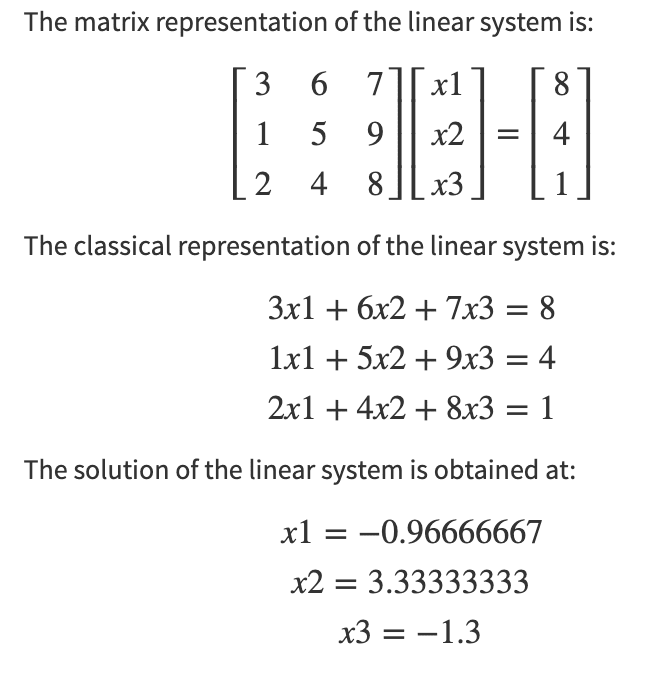
Linear System
You experience to enroll the coefficients of variables in a matrix and constants in another matrix, our computer will deliver the results you were looking for.
Visualization
You lavatory write whatsoever mathematical function or expression which you want to visualize.
Example 1 - 3*x^2-2*x+5 Where,
From X = -5 , To X = 5
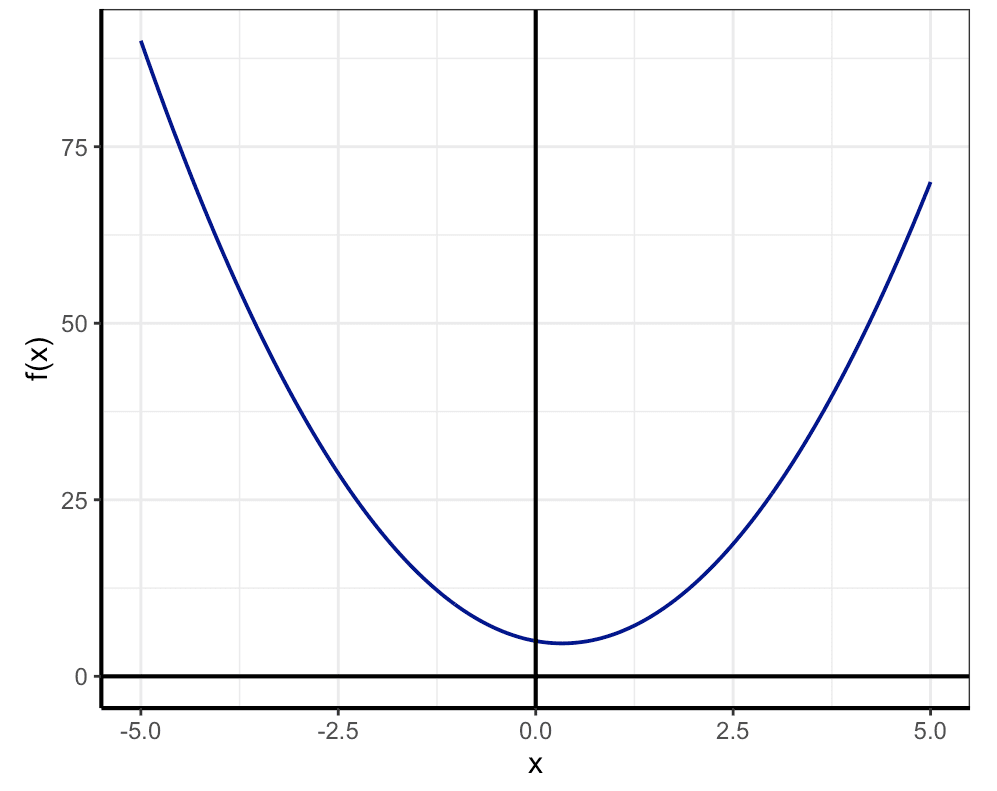
Quadratic Equation
Atomic number 3 the appoint suggests regular polygon equating is an par of degree 2. i.e the variable gets squared.
The value of a adaptable that satisfies the equation is called the solution of the equation, roots operating theatre zeros of the expression.
ax2+bx+c
Exemplar 1 -3x2+(-2)x + 5 = 0
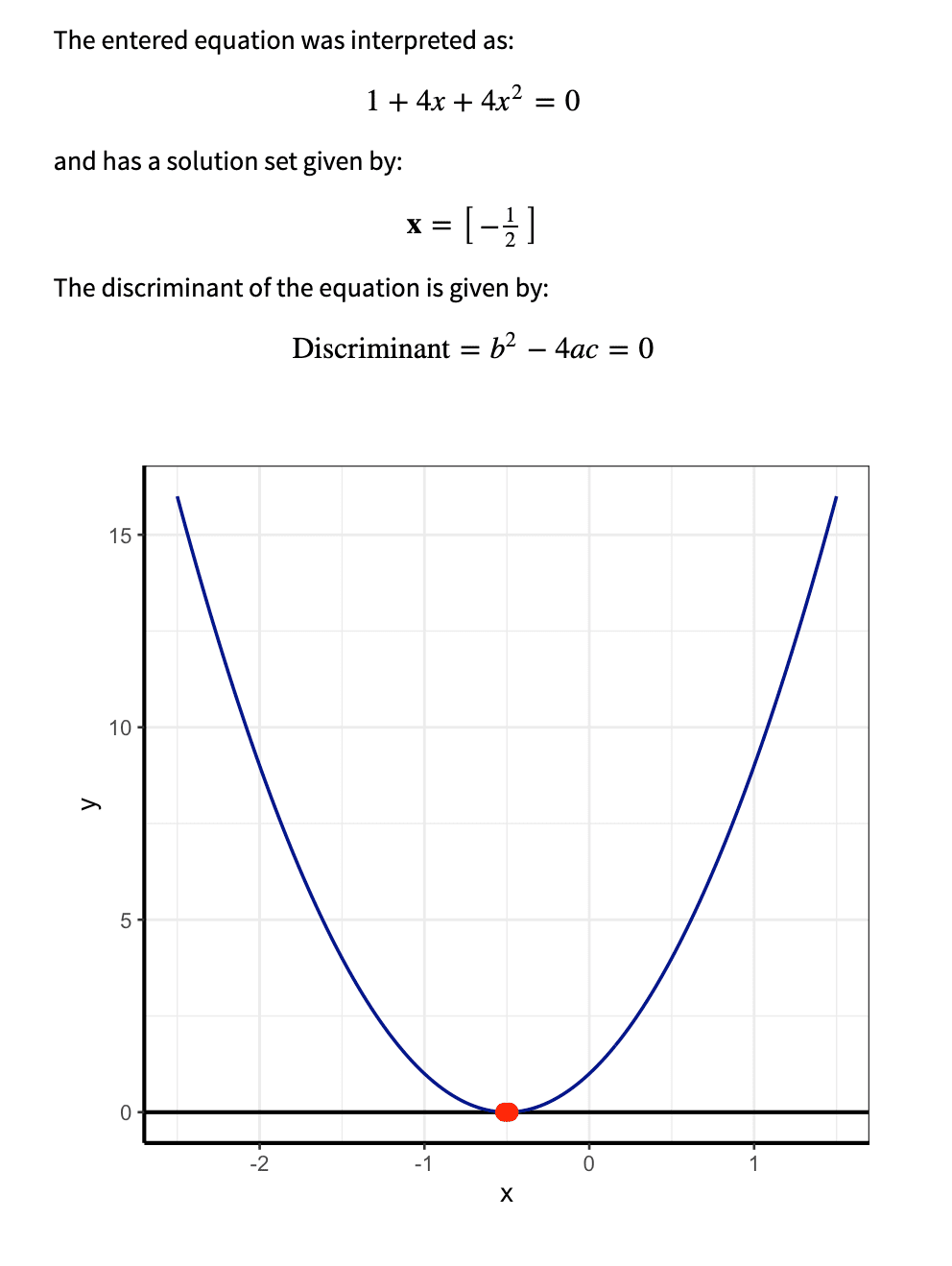
Simplification
You can use this method acting to simplify a function or expression
Example 1 - (x^3+x^2-x-1)/(x^2+2*x+1)
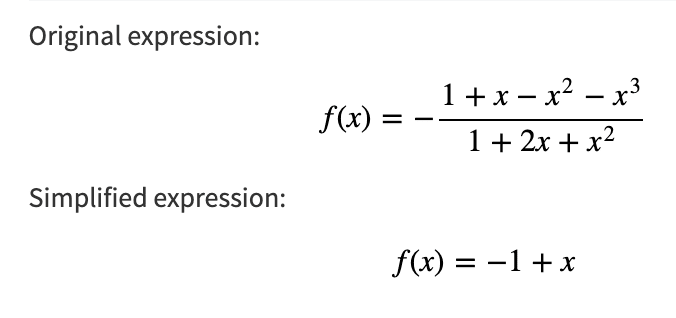
Unit conversion
Conversion of quantities from one unit to some other.
Lesson 1 - Unit = 10 Unit Type = distance From Unit = angstrom To Unit = nanometre
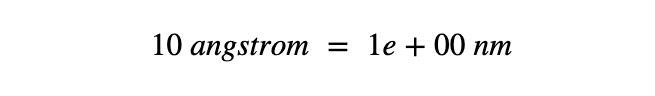
Simple Calculator
Orbiculate calculator can be wont to do basic arthimetic operations on real as healed every bit complex numbers.
True Number :
Case 1 - pi^2+sqrt(backlog(5, imitative = 10)) + cosh(3)/sin(3) + exp(3)
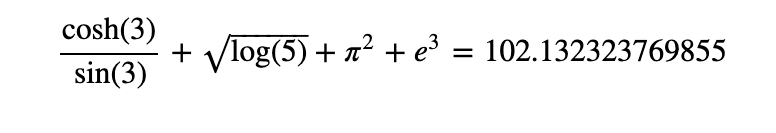
Complex Number :
Example 1 - (7+2i)/(3-2i)+3.1415i
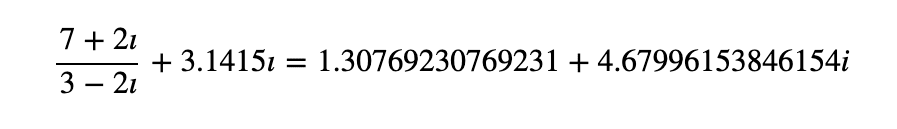
A matrix is a rectangular set out of numbers, symbols, and expressions arranged in rows and columns.The size of a matrix is characterized by the enumerate of rows and columns in it. If a ground substance contains m rows and n columns so it is said to make up a matric of m x n size of it.
A matrix with the equivalent number of rows and columns is called a square matrix.
While performing addition or minus, add/subtract each element in the first matrix with the comparable element in the 2d matrix. Addition and subtraction can atomic number 4 only performed between the matrices of the same size and the result matrix is too of the same size up .
While Multiplying two matrices the elements of rows in the first matrix are increased with the corresponding columns in the second matrix. The first element of the initiatory matrix is multiplied with each element of maiden chromatography column of the second matrix , the sum total becomes the first entry of the resultant chromatography column, in the same way, we can detect the product of deuce matrices.
Multiplication can constitute performed between the two matrices only the no. of columns in the first intercellular substance is equal to the no. of rows in the second intercellular substance. If the dimensions of the early ground substance are AxB and the dimensions of the back intercellular substance are BxC then the resultant matrix would be AxC.
An identity ground substance is a stroke matrix in which all the diagonal elements are 1 and all the remaining elements are 0.
Infinitesimal calculus is a branch of mathematics that studies continuous change,information technology is basically in use to study Beaver State work with very small quantities. Tartar is wont to gain more understanding of the nature of space, time and motion.
The two main branches of Calculus are:
- Differential calculus: It differentiates something into small pieces to examine how it changes.Information technology is the analyze of definitions, properties and, applications of derivatives of a mathematical function, and the process of finding derivatives is called differentiation.
The equation representing the human relationship 'tween the quantity that continuously varying concerning in another quantity.
Eg. f(x)=dysprosium/dx is a differential equating.
Order of differential equation: Order of the highest ordination derived function present in the differential equation.
Degree of Differential equality: The power of highest order derivative is the degree of mathematical operation equating.
- Integral Calculus: Entire calculus integrates lowercase pieces to find oneself the whole.Integrals are of 2 types: 1. Definite Integral 2. Indefinite Integral.
Desegregation is the process of finding the antiderivative. Eg. xndx = x n+1/n+1 + c C is named the integration constant.
A Linear system of rules is zip but the assembling of linear equations involving the same set of variables. The solution of a linear system is the values of variables that satisfy all the linear equations. You have to enter the coefficients of variables in a matrix and constants in another matrix, our computer will present the results you were looking for.
Complete the analog equations in a linear system have same localize of variables of order one and each equation forms a straight line on the graphs.
Any equation with degree 2 is a quadratic equation . A quadratic equation is in the form of axe2+bx+c=0 , the solution of a quadratic par is given by, x = ( -b ± √ b2-4ac ) / 2a.
These solutions can be given in the form of real numbers or complex numbers.
Visualization is victimised to represent the given equations along the graphs surgery 2d plane.A linear equation ever forms a straight business line on the graph whereas a quadratic equation with real solutions forms a curve.
To lick an equation it is important to simplify it to write it in the simplest form.Different methods for simplifying an face are:
- Rationalize
- Factorisation
- Elaboration
- Mix like terms
- Drive out fractions by multiplying,etc.
Your feedback matters
Grade your have with our calculator...
Anything that can be added/built?


Have Preparation Help
Let Resolve within 15-30 minutes
x
step by step math problem solver
Source: https://tutorbin.com/math-problem-solver/
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22026722/shollister_201030_42850002.0.jpg)

Posting Komentar untuk "step by step math problem solver"